WELCOME
What Are Carbon Markets?
A Guide to Voluntary Markets and How They Work

Organizations are rushing to reduce their emissions and meet climate targets
80% of these emissions are made up from carbon dioxide
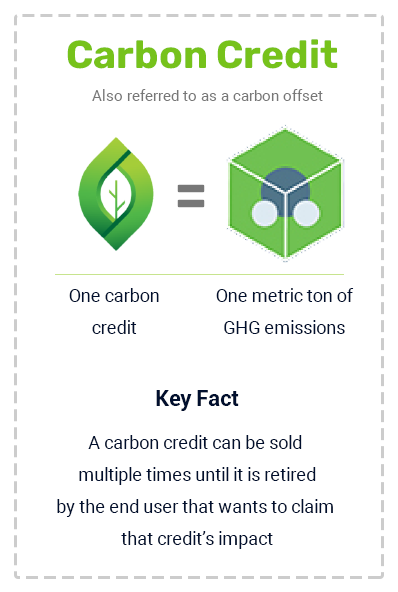
Carbon Footprint
The total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions released into the atmosphere by a company. organization or individual.
Carbon markets play and important role for many companies that want or are required to compensate for their carbon footprint.
TWO MAIN CATEGORIES
Carbon Markets

Compliance Carbon Markets
Mandatory systems regulated by government organizations to cap emissions for specific industries

Voluntary Carbon Markets
Where carbon credits can be purchased by those that voluntarily want to compensate for their emissions
VOLUNTARY CARBON MARKET
Statistics
X
market growth
by 2020
BILLION
VCM quadrupled
since 2020
ORGANSIATIONS
supporting
the VCM
BILLION
Global Carbon
market value
DRIVERS OF
Voluntary Market Demand
01
Paris
Agreement
Companies seeking alignments with these goals
02
Technological Gaps
Companies are limited by technologies that are available at scale and not cost-prohibitive
03
Time
Gaps
Companies do not the the means to eliminate all emissions today
04
Stakeholder Pressure
Companies are facing pressure from stakeholders to address their emissions
Carbon credits are a useful tool to compensate for emissions that cannot currently be eliminated or residual emissions
4 KEY PARTICIPANTS
Voluntary Markets 101
01.
Project Developers
Design and implement carbon offset projects that generate carbon credits that represent emission reductions or removals.
02.
Standard Bodies
Organizations that certify and set the criteria for carbon credits e.g. Verra and the Gold Standard.
03.
Brokers
Intermediaries facilitating carbon credit transactions between buyers and project developers.
03.
End Buyers
Entitiies such as individuals or corporations looking to offset their carbon emissions through purchasing carbon credits.
2 MAIN CATEGORIES
Carbon Offset Projects

Avoidance / Reduction
Prevent or reduce the release of carbon in the atmosphere
e.g Avoided deforestation, fuel -efficient cookstoves

Removal / Sequestration
Remove carbon from the atmosphere
e.g. Reforestation, biochar
Importantly, these carbon offset projects may offer co-benfits, which offer advantages that go beyond carbon reduction or removal:




Biodiversity
Social
Economic
Educational
EXAMPLE PROJECT
Carbontanzania
Location: Madame Savannah
The location of Makame WMA on the southern border of the Tarangire/Manyara ecosystem makes it essential habitat for both endangered and migratory wildlife. The population within the region is rapidly expanding with large numbers of immigrant farmers seeking new land to grow crops and rear livestock. Forests and woodlands are seen as unused and converted to agricultural land. This change in land use has led to a deforestation rate in the area that is 9 times the national average. Land use change threatens the regions extensive biodiversity and has the potential to lead to violent conflict between the traditional users of the land and those seeking to use the natural resources within Makame WMA illegally.
The creation of the Makame Wildlife Management Area (WMA) and its resource plan, has given the Masai communities user-rights over their land and the ability to reserve areas for seasonal grazing. This structure empowers the communities to protect critical grazing areas from illegal immigrant farmers, areas which form the basis of the carbon project.
Employment opportunities for VGS
Environmental education (Carbon Champions)
Control of natural resources to support traditional livelihoods

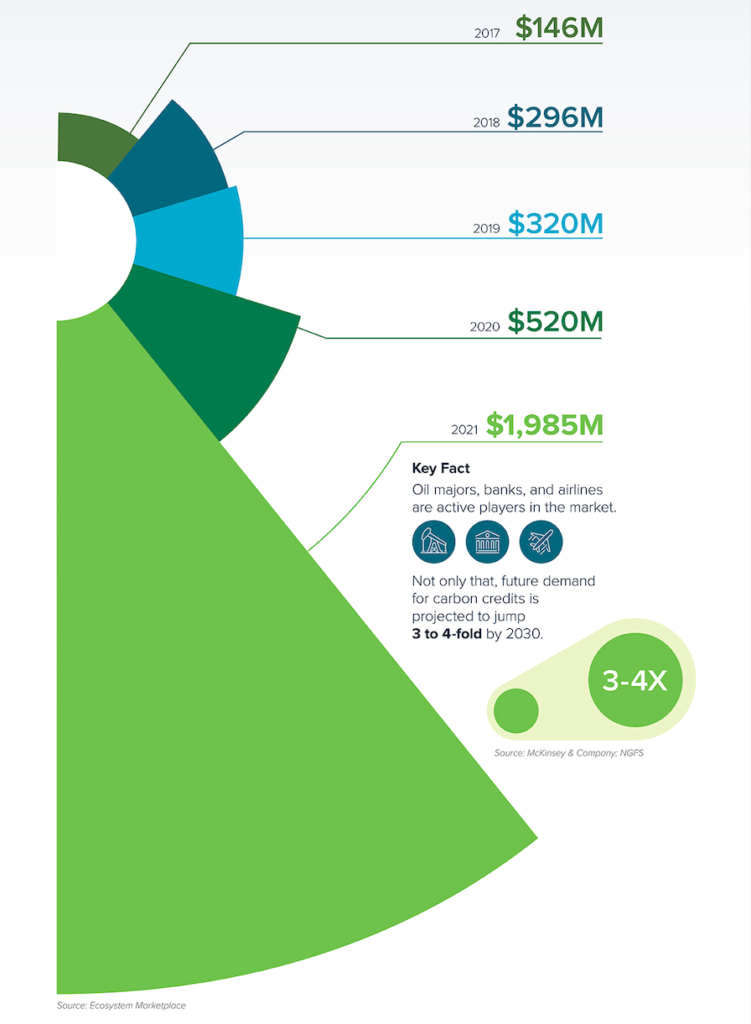
ANNUAL MARKET VALUES ARE INCREASING
Voluntary Markets
WHAT QUALIFIES AS A
High-Quality Carbon Credit?
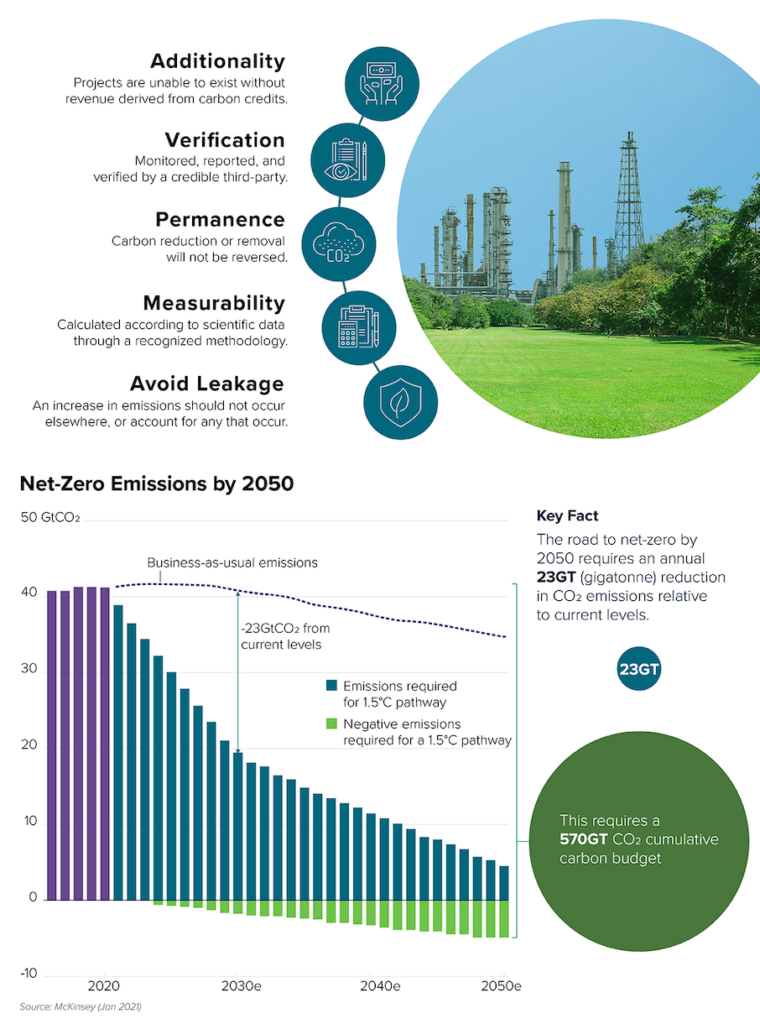
Voluntary markets are playing a critical role in reaching this goal by funding nature based projects, technological advancements and new innovations
